How can societies respond to the impacts of climate change? 4/4
Types of adaptation 2/2
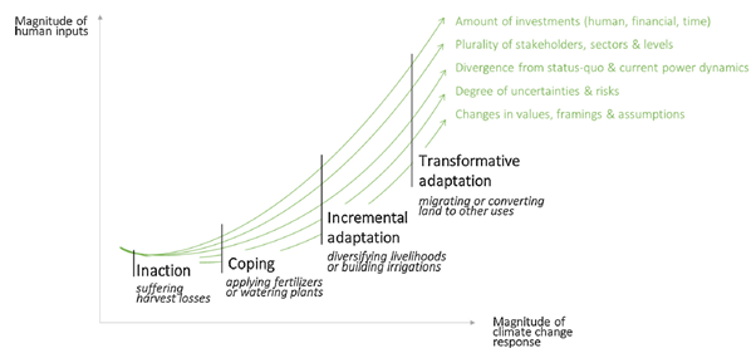
Coping strategies involve short-term, reactive measures to deal with immediate climate impacts. These are often temporary solutions that don’t address the root causes of vulnerability. A good example is using air conditioning during heatwaves without implementing urban heat island mitigation strategies.
Incremental adaptation involves gradual changes to existing systems and practices to reduce vulnerability or enhance resilience to climate change. These measures build upon current approaches and aim to maintain the essence of existing systems. For example, farmers switching to drought-resistant crop varieties.
Finally, transformative adaptation involves fundamental changes to the functioning of a system in response to actual or expected climate change impacts. These long-term measures often lead to new systems or ways of operating. One drastic case could be relocating entire communities from areas at high risk of sea-level rise.
 .
.
Types of adaptation measures, Credits: Fedele et al. 2019
